When it comes to B2B SaaS comparison platforms and companies that review software, G2 stands out. The platform hosts millions of verified user reviews across thousands of tools and services, and it has established itself as the go-to resource for companies to leverage when validating software purchases, as well as building trust in writing for marketers.
But what if you want to scrape data from G2 for analysis at scale, whether to conduct Competitive research includes building a comparison website, running sentiment analysis on reviews, and tracking what customers love (or hate) about your competitors.
In this guide, iWeb Scraping will take you through how to scrape company data from G2 without getting blocked.
- Company listings
- Product reviews
- Alternative tools
- Anti-blocking techniques
But before that let us learn about the reasons why you would even want to scrape G2 initially.
What are the Top Reasons to Scrape G2 Data?
There exists a multitude of reasons you may want to capture structured data from G2, among them:
Competitive Intelligence
You can track how your competitors are being reviewed, what features users are praising, and where they are being criticized. It provides real, unfiltered insights into customer sentiment that can impact your product strategy or marketing messaging.
Review Sentiment Analysis
When looking for reviews to scrape for analysis, you may be a data analyst or simply building your custom dashboard. Scraping G2 reviews allows you to feed real-world sentiment data into your NLP models or create sentiment scores, keyword extractions, or even trends over time.
SEO and Lead Generation
Often, digital marketers create content that compares software or provides reviews of software. In other words, if you can give new G2 data, your content will be more credible and can be monetized on time-on-site to increase your organic rankings.
Create a database of SaaS apps
If you are a founder, curator, or want to create an app directory, you may want to consider creating lists, such as “Top CRM Tools with 4.5+ Stars on G2.” Manual data entry is always tedious and cumbersome; scraping will automate the process.
Scraping G2 Company Project Set-Up
Now that we have discussed the different types of use cases for scraping G2, we can proceed with setting up a scraping project. You will have a basic scraping environment set up and working before you can get started scraping G2. While G2 has a form of bot protection, it is essential to select the appropriate tools to build your scraping environment.
Python Libraries needed
We are going to use:
requests – for static content
- Beautiful Soup – for HTML parsing
- pandas – for saving structured data
- fake_useragent – to randomize headers
- time and random – for delay logic
- playwright (or selenium) – for dynamic pages
Install everything with:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4 pandas fake-useragent playwright playwright install
You can create a basic project structure using:
g2_scraper/ ├── search_scraper.py # Company listings by category ├── reviews_scraper.py # Product review pages ├── alternatives_scraper.py # Competitor tools ├── utils.py
This way, your code looks modular and provides separation, making it easier to manage as your scraping logic expands.
Preventing G2’s Scraping Blockers
Scraping G2 is not as simple as sending requests. G2 uses a combination of anti-bot strategies, like dynamic rendering, rate limiting, and suspicious IP detection. The following are practices for safely and effectively scraping G2.
Rotating User Agents – Do not forget to spoof your browser headers. You can utilize the fake_useragent package to generate random, yet reasonable browser strings.
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
headers = {"User-Agent": UserAgent().random}
Random Delays – You can help keep bots away by introducing random, human-like delays between your calls.
import time, random time.sleep(random.uniform(2, 5))
Headless Browsers for JavaScript Pages – G2 serves up review and comparison pages that are client-side rendered. Use Playwright or Selenium to call the page and fetch all the page content without issue.
Residential or Rotating Proxies – If you are scraping large amounts of data, then you should purchase proxy services if you are scraping on a large scale. Rotating proxies will mask your IP address and help protect you from being blocked.
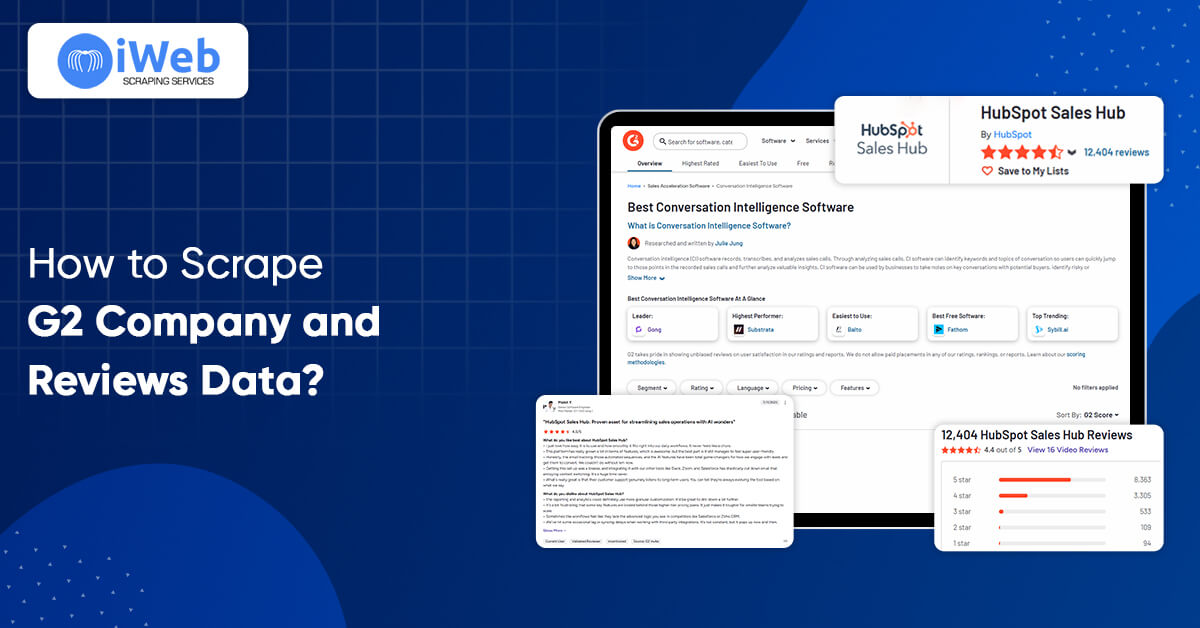
Scraping G2 Company Listings
G2 serves companies by category, such as CRM, Marketing Automation, and Project Management. All categories have numerous pages of software cards that link to the product detail page.
URL Structure
https://www.g2.com/categories/[category-name]?page=1
Data Points to Parse
You will want to parse the following data points from each company card:
- Software name
- URL to the company profile
- Star rating
- Total reviews
- Tags or category labels
Sample Code:
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from fake_useragent import UserAgent
def scrape_search_page(category, page=1):
url = f"https://www.g2.com/categories/{category}?page={page}"
headers = {"User-Agent": UserAgent().random}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(r.text, "html.parser")
cards = soup.select("div.software-card")
for card in cards:
name = card.select_one("h3.software-name").text.strip()
link = "https://www.g2.com" + card.select_one("a")['href']
print(f"{name}: {link}")
You can then rinse and repeat this process for your additional pages or categories, and store the results in a CSV file for future crawling.
Scraping G2 Reviews for a Company
Note: the review section of the page loads asynchronously. So you can’t use requests and scrape it that way. You will want to use Playwright to load the JavaScript.
URL Structure
https://www.g2.com/products/[product-slug]/reviews
What to Parse
We want to scrape/parse:
- Review title
- Star rating
- Review body
- Pros and Cons
- Job title and industry of the reviewer
- Review dat
Here is a sample code using Playwright.
from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
import pandas as pd
def scrape_reviews(product_slug):
data = []
with sync_playwright() as p:
browser = p.chromium.launch(headless=True)
page = browser.new_page()
page.goto(f"https://www.g2.com/products/{product_slug}/reviews")
page.wait_for_selector(".review-card")
cards = page.query_selector_all(".review-card")
for card in cards:
title = card.query_selector(".review-title").inner_text()
rating = card.query_selector(".star-rating").get_attribute("data-rating")
body = card.query_selector(".review-body").inner_text()
data.append({"title": title, "rating": rating, "body": body})
return pd.DataFrame(data)
df = scrape_reviews("hubspot-marketing-hub")
df.to_csv("hubspot_reviews.csv", index=False)
You can scroll or paginate in Playwright to get more reviews, etc.
Scraping G2 Alternatives
Each G2 product page features an Alternatives component that displays tools with similar features.
URL Structure
https://www.g2.com/products/[product-slug]/competitors
This page is often populated dynamically as well, so you will want to utilize Playwright again.
Data to Parse
For this part, you will want to scrape/parse:
- Alternative product names
- Comparison highlights (i.e., higher rating, lower price, more features)
- Link to competitor page
Sample Code
def scrape_alternatives(product_slug):
with sync_playwright() as p:
browser = p.chromium.launch()
page = browser.new_page()
page.goto(f"https://www.g2.com/products/{product_slug}/competitors")
page.wait_for_selector(".software-card")
cards = page.query_selector_all(".software-card")
for card in cards:
name = card.query_selector("h3").inner_text()
print("Alternative:", name)
You can then use this data to create all your competitor maps with it, or to generate SEO content, such as ‘Best Alternatives to [Tool].’
Storing Data for Further Analysis
After you have collected your data, you can use pandas to save it into CSV, JSON, or even push all the data to a database for long-term data storage.
df.to_csv("g2_reviews.csv", index=False)
df.to_json("g2_reviews.json", orient="records")
You can then analyze the data using Python, Excel, or feed it into your BI tools.
Final Thoughts & Best Practices
Scraping G2 can provide a wealth of data for businesses, but it should be done responsibly and with ample forethought. Always understand G2’s Terms of Use, since we can only use the data for research or internal purposes. When scraping a website, it is always best to set limits on your crawlers to prevent overloading their services and risk getting blocked or throttled. Additionally, for enterprise or long-term scraping, it is essential to consider using proxies and headless browsers to conduct the scrapes, simulating human behavior and thereby avoiding suppression systems.
G2 can update its site structure without notice, so maintaining regular check-ins on your code and records is essential to keep your data up to date. Regularly testing your scraping scripts and adjusting them as necessary will help mitigate issues caused by changes in the website’s layout or functionality. This vigilance ensures that your data remains reliable and relevant for your analysis or business needs.
Final Thoughts
At iWeb Scraping, we specialize in extracting data from vibrant, complex, and high-return sites, such as G2 or others. We can extract G2 data at scale with high precision, accuracy, and reliability. Whether you want to extract millions of user reviews, conduct live pricing comparisons linked to all relevant competitor details, or build custom inbound API endpoints to update the data, we have all the services to meet those needs.
Let us know what we can do for you, and we will handle your G2 scraping hassle-free, on time, at scale, and 100% reliably!
 Parth Vataliya
Parth Vataliya