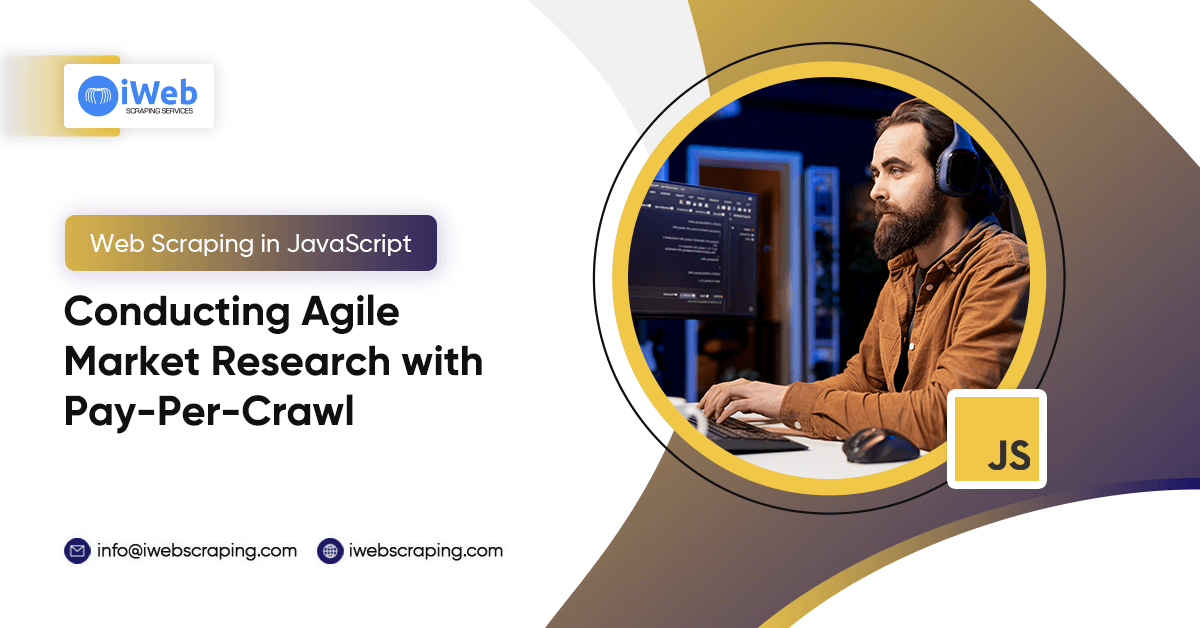
Web scraping has become an indispensable skill for modern developers. Whether you’re building price comparison tools, monitoring competitor data, or aggregating content from multiple sources, JavaScript provides powerful capabilities to extract web data efficiently. This comprehensive guide explores the essential techniques every developer needs to master web scraping with JavaScript.
Understanding Web Scraping Fundamentals
Web scraping involves extracting data from websites programmatically. Instead of manually copying information, developers use automated scripts to gather structured data at scale. JavaScript has emerged as a preferred language for this task because it handles dynamic content seamlessly and offers robust libraries for data extraction.
Moreover, JavaScript runs in both browser and server environments, giving developers flexibility in their scraping approach. Companies like iwebscraping.com leverage these techniques to help businesses gather competitive intelligence and market research data effectively.
However, before diving into technical implementations, you must understand the legal and ethical considerations. Always respect robots.txt files, avoid overwhelming servers with requests, and comply with website terms of service.
Choosing the Right JavaScript Tools for Web Scraping
Several powerful libraries simplify web scraping tasks in JavaScript. Each tool serves different purposes based on your project requirements.
Node.js and Essential Libraries
Node.js provides the foundation for server-side scraping operations. It allows you to run JavaScript outside the browser environment, making it perfect for automated data extraction tasks.
- Axios: Handles HTTP requests efficiently. This library sends GET and POST requests to fetch webpage content. It supports promises and async/await syntax, making your code cleaner and more maintainable.
- Cheerio: Parses HTML with jQuery-like syntax. Developers familiar with jQuery can start scraping immediately without learning new APIs. Cheerio loads HTML into memory and lets you traverse the DOM structure using familiar selectors.
- Puppeteer: Controls headless Chrome browsers. This Google-maintained library handles JavaScript-heavy websites that render content dynamically. Unlike simple HTTP requests, Puppeteer executes JavaScript code on pages before extracting data.
When to Use Each Tool
Use Axios and Cheerio for static websites. These sites serve complete HTML in the initial response. This combination works efficiently for blogs, news sites, and simple e-commerce platforms.
Meanwhile, choose Puppeteer for dynamic applications. Modern web apps using React, Vue, or Angular require JavaScript execution to display content. Puppeteer renders pages fully before scraping begins.
iwebscraping.com professionals recommend starting with simpler tools first. If basic HTTP requests don’t retrieve needed data, then escalate to browser automation.
Scraping Static Websites with Axios and Cheerio
Static websites are the easiest targets for web scraping. They deliver complete HTML content in server responses without requiring JavaScript execution.
Setting Up Your Environment
First, initialize a new Node.js project. Open your terminal and create a project directory:
npm init -y npm install axios cheerio
This command installs both libraries as dependencies. Now you’re ready to write your first scraper.
Building a Basic Scraper
Create a new file called scraper.js. This simple example extracts article titles from a blog:
The scraper sends an HTTP request using Axios. Once the response arrives, Cheerio parses the HTML. You can then select elements using CSS selectors, just like in jQuery. Finally, the script extracts text content and stores it in an array.
Handling Data Extraction Efficiently
Extract data systematically by identifying consistent HTML patterns. Inspect the target website’s structure using browser developer tools. Look for unique class names, IDs, or semantic HTML tags that contain your desired information.
Furthermore, websites often use structured data formats like JSON-LD or microdata. These formats make extraction more reliable because they’re specifically designed for machines to read.
Consider error handling at every step. Network failures, changed HTML structures, or missing elements can break your scraper. Wrap your code in try-catch blocks and implement retry logic for failed requests.
Scraping Dynamic Websites with Puppeteer
Dynamic websites present unique challenges. They load initial HTML shells and then populate content using JavaScript. Traditional HTTP requests only capture the shell, missing the actual data.
Understanding Dynamic Content Loading
Single-page applications (SPAs) fetch data through API calls after page load. Social media feeds, infinite scroll pages, and interactive dashboards all use this approach. Therefore, your scraper must wait for JavaScript execution before extracting content.
Puppeteer solves this problem by launching a real browser instance. It navigates to pages, waits for content to load, and then extracts fully rendered HTML.
Implementing Puppeteer Scrapers
Install Puppeteer in your project:
npm install puppeteer
Puppeteer automatically downloads a compatible Chromium version. This ensures consistency across different environments.
Here’s how to scrape a dynamic website:
The script launches a headless browser, navigates to the target URL, and waits for specific elements to appear. Once loaded, it evaluates JavaScript in the page context to extract data. This approach handles any dynamic content reliably.
Optimizing Puppeteer Performance
Puppeteer consumes significant memory and CPU resources. Each browser instance requires hundreds of megabytes of RAM. However, several optimization techniques improve performance.
Reuse browser instances across multiple scraping tasks. Launching browsers is expensive, so create one instance and open new pages within it. Additionally, disable unnecessary features like images and CSS when you only need text data.
Set appropriate timeouts for page loads. Some pages load slowly or contain broken resources. Configure maximum wait times to prevent your scraper from hanging indefinitely.
iwebscraping.com experts implement request throttling and browser pooling for large-scale operations. These techniques balance speed with resource constraints effectively.
Handling Common Scraping Challenges
Web scraping rarely works perfectly on the first attempt. Developers encounter various obstacles that require creative solutions.
Dealing with Rate Limiting
Websites protect themselves from aggressive scrapers using rate limits. Sending too many requests quickly results in blocked IP addresses or temporary bans.
Implement delays between requests to mimic human behavior. Random delays between 1-3 seconds work well for most scenarios. Furthermore, rotate user agents to appear as different browsers.
For extensive scraping projects, consider using proxy rotation. Proxies distribute requests across multiple IP addresses, preventing blocks. Services like those offered through iwebscraping.com provide managed proxy solutions.
Navigating Authentication Requirements
Many websites require login credentials to access content. Puppeteer handles authentication workflows effectively.
Automate login forms by filling input fields and clicking submit buttons. Wait for successful authentication before proceeding to scrape protected pages. Store session cookies to avoid repeated logins during the same scraping session.
However, be aware that scraping authenticated content raises additional legal concerns. Always verify that your use case complies with terms of service.
Parsing Complex HTML Structures
Real-world websites contain messy, inconsistent HTML. Nested tables, dynamic class names, and redundant markup complicate data extraction.
Use multiple selectors as fallbacks. If your primary selector fails, try alternative approaches. Regular expressions help clean extracted text by removing whitespace, special characters, or unwanted formatting.
Additionally, consider the website’s responsiveness. Many sites serve different HTML to mobile and desktop users. Choose the version that provides cleaner, more accessible markup.
Best Practices for Production Scrapers
Building reliable, maintainable scrapers requires following established best practices. These guidelines ensure your code remains robust as websites evolve.
Implementing Robust Error Handling
Network failures happen frequently in web scraping. Servers go down, connections timeout, and responses return unexpected formats. Therefore, comprehensive error handling is essential.
Network failures happen frequently in web scraping. Servers go down, connections timeout, and responses return unexpected formats. Therefore, comprehensive error handling is essential.
Implement automatic retry logic with exponential backoff. If a request fails, wait briefly and try again. Increase wait times with each subsequent failure to avoid hammering problematic servers.
Storing Scraped Data Efficiently
Choose appropriate storage solutions based on your data volume and structure. Small datasets work fine in JSON or CSV files. Larger projects benefit from databases like MongoDB or PostgreSQL.
Normalize data during extraction to maintain consistency. Convert dates to standard formats, clean phone numbers, and standardize addresses. Clean data reduces processing requirements downstream.
Moreover, implement deduplication logic to avoid storing the same information multiple times. Hash key fields and check for existing records before inserting new data.
Monitoring Scraper Health
Production scrapers require ongoing monitoring. Websites change their structure regularly, breaking existing scrapers without warning.
Set up automated alerts when scrapers fail or return unexpected results. Monitor success rates, execution times, and data quality metrics. This proactive approach minimizes downtime.
iwebscraping.com provides managed scraping services that include 24/7 monitoring and automatic maintenance. These services ensure continuous data flow even as target websites evolve.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Web scraping exists in a complex legal landscape. Understanding these considerations protects your projects from legal challenges.
Respecting Robots.txt
The robots.txt file tells scrapers which parts of a website they can access. Ethical developers always check this file before scraping. Located at the site’s root (domain.com/robots.txt), it specifies allowed and disallowed paths.
Parse robots.txt programmatically in your scrapers. Libraries like robots-parser automate this check. Skip disallowed URLs to respect website owners’ wishes.
Understanding Terms of Service
Many websites explicitly prohibit scraping in their terms of service. Review these terms carefully before starting any project. Violating terms of service can result in legal action, even if you’re scraping publicly available data.
Consider reaching out to website owners when possible. Some companies provide official APIs or data partnerships. These legitimate channels often deliver higher quality data with legal protection.
Protecting Personal Information
Scraping personal data triggers privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. These laws impose strict requirements on data collection, storage, and usage.
Limit data collection to what you actually need. Avoid scraping sensitive personal information unless absolutely necessary and legally permitted. Implement proper security measures to protect any collected data.
Advancing Your Web Scraping Skills
Mastering web scraping requires continuous learning and practice. Start with simple projects and gradually tackle more complex challenges.
Build a portfolio of scraping projects demonstrating various techniques. Extract product data from e-commerce sites, monitor news sources, or aggregate real estate listings. These practical experiences develop problem-solving skills.
Join developer communities focused on web scraping. Forums, GitHub repositories, and specialized platforms connect you with experienced practitioners. Learning from others’ challenges and solutions accelerates your growth.
Furthermore, stay updated on new tools and techniques. The web scraping landscape evolves constantly with new libraries, browser capabilities, and anti-scraping measures. Following industry leaders and companies like iwebscraping.com keeps you informed about emerging trends.
Conclusion
Web scraping with JavaScript opens powerful possibilities for data-driven applications. Whether you’re using Axios and Cheerio for static sites or Puppeteer for dynamic content, JavaScript provides robust tools for every scenario.
Success in web scraping combines technical skills with ethical awareness. Build reliable scrapers that respect website resources, follow legal guidelines, and deliver clean, actionable data. By mastering these essential techniques, you’ll add valuable capabilities to your development toolkit.
Ready to implement professional web scraping solutions? Explore how iWeb Scraping can help your business extract and leverage web data effectively. With the right approach and tools, web scraping becomes a strategic advantage in today’s data-driven world.
 Parth Vataliya
Parth Vataliya